INSTITUTE OF PHILOSOPHY OF NATURE
Abstract
The wave particle duality accepted for light is conceptually inconsistent and against the consistent norms of nature. Light is conceptualized differently in different contexts such as light is a wave packet, a point particle, a field excitation but there is no definite consensus for any one of these concepts. It is also postulated that light waves do not require a medium which is far from reality. On the other hand, the particle concept of light is feasible therefore is a reality, however, it fails to explain many phenomena of light. The fault lies with the defective understanding of the structure of the light particle, the ignorance of the non-electric charge state of the light particle and the structure & non-electric charge field in the medium and in the interface. Light particles while moving from one medium to another medium essentially pass through the interface of the mediums where it exhibits different phenomena such as reflection, refraction of light. Thus, a clear understanding of the structure and field of the interface becomes a vital issue for the field particle interaction in interpreting the surface phenomena of light. In macro scale the interface has zero thickness but in micro domain scale its thickness spreads to few atomic dimensions. Again, the interface thickness becomes infinite in micro-micro domain scale (photonic scale). Thus, a light particle has enough room for its dynamics in the photonic charge field within the interface. The photonic charge field within the structure of the interface medium is formed by micro-micro domain space matter particles (light particles). In the new concept, the light particles have rest mass, mass-space structure and carry photonic charge and the interface zone has a photonic charge field. While the new model of light particles and the new understanding of interface have scope of explaining all phenomena of light, this paper explains the reflection & refraction of light from classical analysis.
Key words: Micro-micro structure, Light particles, Reflection of light, Refraction of light,
Wave particle duality, Wave packet, Point particle, Field excitation.
Discussion
The universe is a continuum of mass-space systems, where mass contains space and space contains space-matter-particles [1]. Space has a continuum in the universe and matter has discrete form in it. Due to mass-space interaction, any discrete form of matter remains connected with other matters of the universe. Discrete matter is surrounded by a space medium therefore the surface of matter (solid or liquid) is essentially the interface between matter and space or between any two types of matter with different density. At the macroscopic scale, the interface is treated as having zero thickness. In the micro-domain scale, the same interface extends over a few atomic dimensions. At the micro-micro domain scale, the interface no longer has a finite boundary and effectively spreads over an infinite thickness (Fig.1). The interface structure is influenced by the structures of two interfacing mediums.
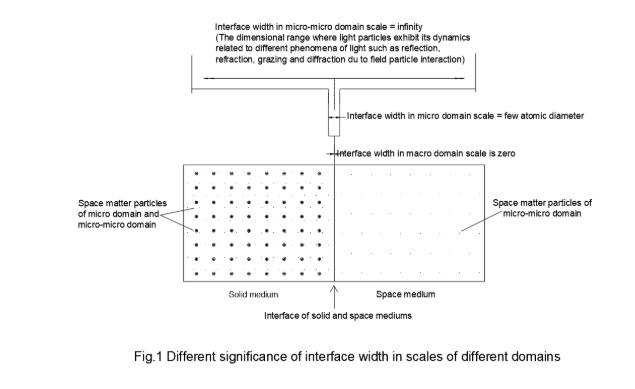
At present the structural component of matter is limited to micro particles hence the conceptualized structure is limited to micro structure and the charge field is limited to electric field. Thus, it is difficult to perceive the micro structure of the thin interface comprising micro particles and the electric field within it. The present author has introduced the rest mass of micro-micro domain particles (light particles) and their non-electric charge state (photonic charge state) [2], [3]. This opens up new avenues on the existence of micro-micro domain structure within a micro structure or a self-standing micro-micro structure in space/vacuum.
The micro-micro domain structure within the micro structure of the interfacing mediums also contains micro-micro particles in free-state carrying photonic charge similar to the existence of free electrons in micro structure. The two interfacing surfaces have different number densities of micro-micro domain particles carrying photonic charge in free-state and form a stiff photonic charge potential gradient within the interface. Thus, a strong photonic field exists within the interface due to the stiff potential gradient in micro-micro domain scale which takes part in field particle interaction in rendering different surface phenomena of light particles. The newly identified micro-micro structure of the interface having a strong photonic charge field plays a vital role in the new classical dynamics of light particles carrying photonic charge. The revamped classical physics has a great scope for analysing the different phenomena of light from field-particle interaction.
Existing concept of light particle
In modern physics, the light particle is called a photon. It emerges from quantum electrodynamics (QED) and is clubbed with the classical electromagnetic wave theory and quantum mechanics. It is not a particle in the classical sense thus it has no volume, radius, or internal structure but behaves like a particle. Light is also considered as a wave. Again, the light wave is not a classical wave but behaves like a wave. Light waves exist even without a medium. The light particles are conceptualised to have momentum without mass, spin without a geometrical form and charge-neutral without the knowledge of non-electric charge. Light particles have a constant velocity without slowing down or speeding up and cannot turn around through v → 0 → –v like classical objects. Light is conceptualized differently such as light is a wave packet, a point particle, a field excitation for different purposes but there is no definite consensus for any one of these concepts.
Structures of light particle and medium in the new concept
The wave particle duality accepted for light in modern science is conceptually inconsistent and against the consistent norms of nature. While analysing different phenomena of light we make use of classical terminologies such as particle, wave, momentum etc. each having specific significance in macro domain that justifies the defined terms but in micro domain, scientists have used the terminologies of macro domain physics while liberally altering the defined parameters that qualify their stand. For example, particle in any domain has to have the aspect properties of particle (mass, structure etc.) and the medium has to have the necessary modulus of elasticity if it has to execute the light wave. No doubt, the unnatural assumptions coupled with the unnatural theoretical treatment yields results but this can’t be the confirmation of the assumptions or the theory describing different aspects of nature. On the other hand, one can’t rule out the possibility of new theoretical analysis of classical physics with the consideration of less-known objects and events of micro-micro domain for understanding the micro domain physics and different phenomena of light in a natural manner.
In the new concept, light particles have mass in the photonic mass unit [4], mass-space structure with nucleus and extra-nuclear space structure [5], charge in photonic charge units [3], spin and energy with energy level [6]. The space medium also has a fine structure comprising micro-micro particles (light particles and other field forming particles) as space matter particles. Thus, classical physics has a new scope of dealing with micro domain physics and micro-micro domain physics in a clear conceptual manner. Proper insight into the existence of matter in finer and finer domains, below micro domain provides new scope of understanding micro phenomena and the phenomena of light while retaining the commonsense knowledge and the cause-to-effect analogy [7]. If the natural concept with mathematical analysis can yield results, then there is no need to pursue a mathematical concept with mathematical analysis. If the straightforward answer is interpretable in the natural manner from classical physics, then we may not have to make unnatural hypotheses to interpret the reality. When all sciences are aimed at discovering the reality of nature, modern science alone stands on a different footing by keeping aside the commonsense knowledge and cause-to-effect analogy. Appropriate modification of the concepts of micro-domain science and the theory of light would help to reframe the science in the light of reality. Thereafter, finding harmony among different sciences would not be a problem since the basic assumptions in all sciences remain the same. The dynamics of classical physics is enough to explain different phenomena of light with the insight to micro-micro domain structure and the non-electric charge of light particles.
Any solid object has a boundary which is recognized as the surface of the object. There exists another medium beyond the boundary of the solid which may be solid, liquid, gas or space having different density. Thus, what we normally refer as the surface, in reality, refers only to the interface of two different mediums such as solid-solid interface, solid-liquid interface, solid-gas interface, solid-space interface, liquid-liquid interface (immiscible liquids), liquid-gas interface, liquid-space interface. All forms of macro matter are known to have been composed of microscopic atoms. Thus, a smooth surface in macroscopic scale has a rough surface with high degree of unevenness in microscopic scale due to the discrete placement of surface atoms (Fig.2).
A football with spherical surface in macro scale can rebound from a flat macro surface made of atoms obeying the law of rebound i.e. the angle of approach equal to the angle of rebound (Fig.3).
However, if a football is made to rebound from the surface of a solid formed by packing of footballs, it will not obey the law of rebound. Likewise, if a micro particle is made to reflect from a smooth flat macro surface, theoretically it should not obey the law
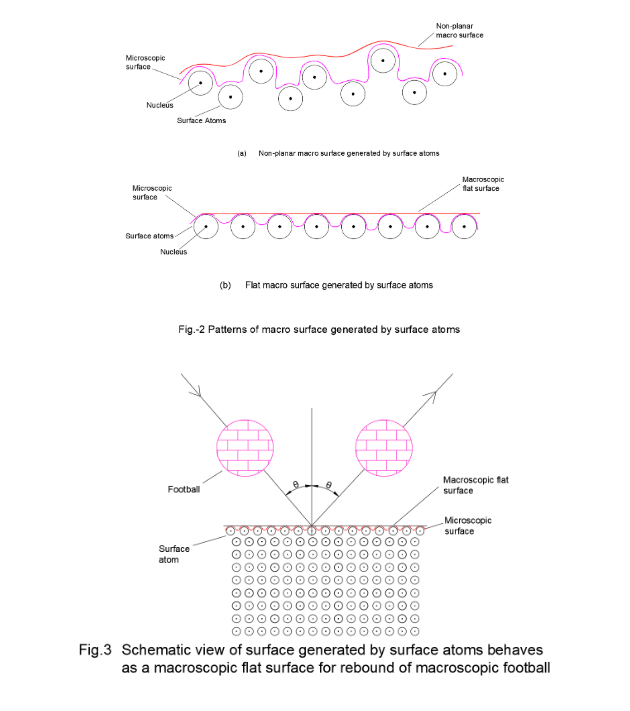
of reflection since the reflecting surface is very uneven in microscopic scale. But in reality, the micro particles (atomic particles) and the micro-micro particles (light particles) are seen reflecting from a smooth macro surface even though the surface is very rough in microscopic scale and very-very rough in micro-microscopic scale. Theoretically it is impossible to expect the optical flatness of a surface built up by atomic particles. Even when we consider the surface is formed by micro-micro domain particles, then also the surface can’t have the optical flatness for reflection of light particles because the surface remains rough in micro-micro domain scale. This breeds doubt on particle theory of light. On the other hand, we can’t accept the wave concept of light since light waves are just not feasible without a medium or with a medium not having the required modulus of elasticity for propagation of waves. Hence the wave concept is unthinkable. Thus, the natural phenomena of light cannot be justified following the unnatural wave theory of light. However, the particle concept of light being feasible and realistic remains as the only way to understand the reflection and refraction of light. Hence, it is required to understand the true significance of optical flatness of the interface.
For conceptualizing the significance of optical flatness, we may examine the extra-nuclear space structure of a celestial body (say the earth), close to the surface of the earth. There exist a polarized electric potential structure and a polarized photonic charge structure (thermal charge structure) in the extra-nuclear space structure of the earth near the surface [8]. The electric charge polarized structure in the (atmosphere) of a macro celestial body is formed by the electric charge interaction and gravity in the di-electric air medium [8]. In the like manner the photonic charge polarized structure forms within the interface medium due to electric and photonic charge interactions (Fig.4).
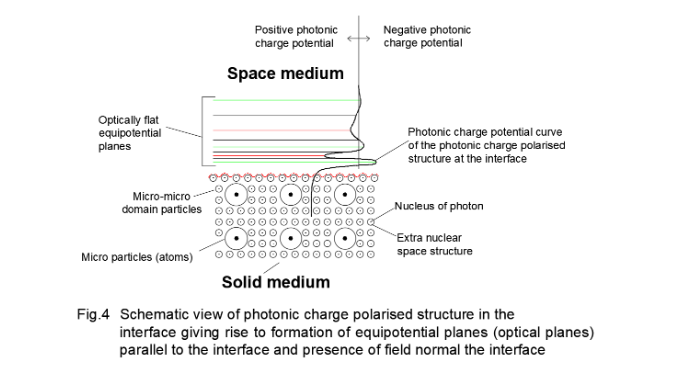
The surface of the earth is quite uneven in macroscopic scale due to the existence of mountains and valleys but the E and F layers of ionospheres are evenly smooth. Definite electromagnetic emissions are reflected from the smooth curvatures of E and F layers of the ionosphere obeying the law of reflection. It is rational to assume that the radiation particles are reflected from the equipotential parallel planes in the charge field barrier which behaves as an optically smooth spherical plane despite the uneven surface of the earth. The field-particle-interaction observed in the ionosphere of the earth is quite tempting for understanding the reflection of light from the photonic field barrier within the interface. Even though the surface of the earth is rough, the ionospheric electron density curve of the E & F layer remains smooth (excluding the variation during the time of the day). One can anticipate polarized photonic charge potential layers within the interface that provides the optical flatness even though the morphology of the atomic front is non-planar in macroscopic and microscopic scales.
In the new concept, light particles have mass and structure in photonic scale units with a nucleus and extra nuclear space structure similar to the structure and features of the new atomic system or the solar system [5]. The light particles of micro-micro domain form the less known micro-micro structure in micro particles and macro bodies. Hence, a macro body has co-existing structures in three domains (macro structure, micro structure and micro-micro structure) (Fig.5) and the same is also discussed elsewhere [4].

The micro-micro structure of matter exists in the extra nuclear space structure of atoms and in the inter atomic space. Thus, the micro-micro particles have a great role in forming the fine structure of any surface/interface. This aspect is ignored in the present concept. According to the present science, the surface atoms are considered to have unsatisfied-bond or “dangling bonds” due to the unsymmetrical placement of neighbouring atoms. The dangling bond of the surface atoms associates unpaired electron density localized near the surface atom. This causes charge polarization in the surface atoms. The polarized surface atom produces an electric field within the proximity of adjacent gaseous/space medium which modifies the surface features in a broad sense [9].
The surface states and polarization produce localized electric fields responsible for surface potential barriers (Schottky barriers). These fields are extremely localized (typically over a few angstroms) and give rise to a surface potential barrier [10]. In the new three domain structure of solid, the surface photons of micro-micro domain structure may be anticipated to produce photonic charge polarized fields at the interface. Like the surface electric field, the photonic field may be considered localized that gives rise to the formation of a photonic charge field barrier at the surface/interface. The flat macroscopic surface generated by the micro particles of micro structure is rough in micro domain scale. Similarly, the flat microscopic surface generated by micro-micro particles of micro-micro structure is rough in micro-micro domain scale and the flat micro-micro structure is rough in micro-micro domain scale. But the photonic equipotential planes within the photonic field remain optically flat in micro-micro domain scale.
The surface of a solid has a new significance with the consideration of a new micro-micro structure of the interface zone. The interface structure is composed of micro-micro domain particles which is distinctly different from the structures of the interfacing mediums comprising particles of micro domain and micro-micro domain (Fig.6(a) Fig.6(b)).
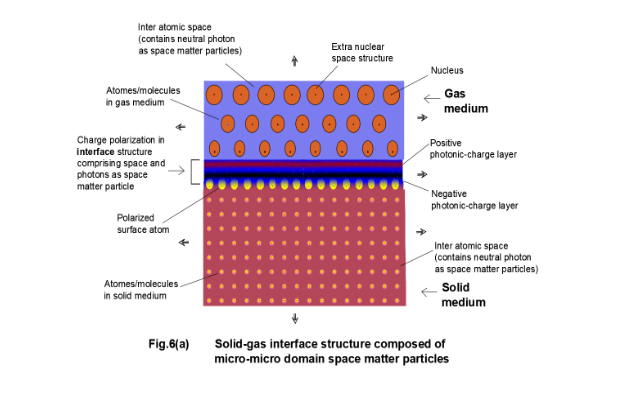
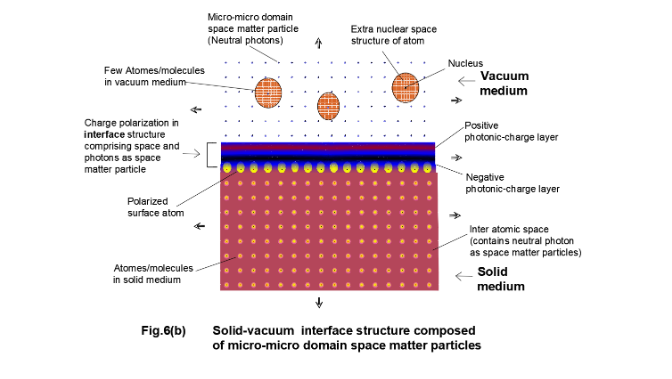
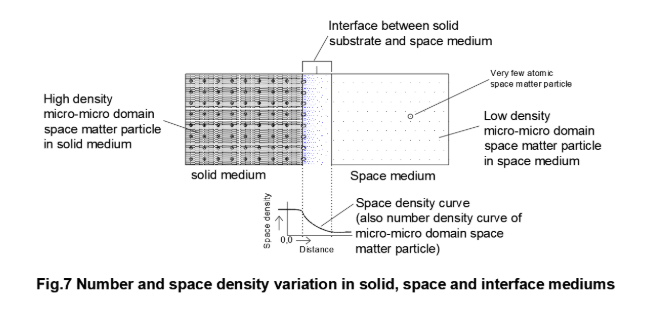
The thickness of the structured interface in micro-micro domain scale is quite large to visualize the fine structures of the interface and the field present in it. The interface structure is different from the structure of dense solid phase and the structure of gaseous phase or vacuum. Few atomic layers in both the interfacing mediums are also affected due to the strong field at the interface. The space density and the number density of the space matter particles vary spatially within the interface (Fig.7).
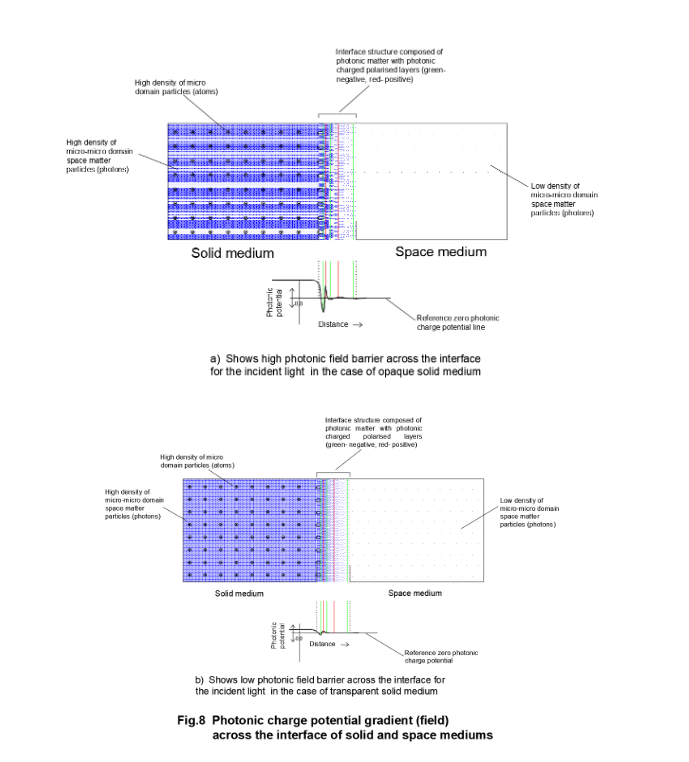
The strong photonic field prevailing in the interface fluid (photonic fluid) forms a plurality of photonic charge polarized layers in micro-micro domain scale within the interface which plays the primary role for different surface phenomena of light. The photonic charge-polarized planes within the interface are optically flat for the reflection and refraction of light particles. In the new interpretation, the unrealistic wave concept of light becomes redundant.
The interaction of photon with polarized photonic charge field barriers
The earth is a solid body and has its extra-nuclear structure (atmosphere). Beyond the extra nuclear structure of the earth the space medium belongs to the extra nuclear space structure of the sun. The nature of structure of the atmosphere of the earth is a direct realization of the interface structure between solid earth and the space medium. The extra nuclear space structure of the earth contains space matter particles which are atoms and molecules. The number density of space matter particles is highest at the surface of the earth and decreases towards the boundary of the terrestrial system. Further the size of space matter particles goes on decreasing towards the boundary. This predicts the existence of finer and finer atoms below hydrogen atom [Appendix-1] as space matter particles in the outer part of extra nuclear space structure of the earth.
Different light particles with different energy levels enter to different depths of the polarized field and are reflected from there. But in the case of transparent material the polarized field barrier is reduced due to conductivity of photons, like the polarized electric charge is not feasible in a conducting material. The light particles entering the body of transparent material at an angle with the normal, change their path in the photonic field of the interface.
The co-existence of micro structure and micro-macro structure within a macro solid medium envisions the presence of electric charge interaction for the formation and stability of micro structure and the photonic charge interactions for the formation and stability of micro-micro structure. There exists electric charge potential within inter atomic space and photonic charge potential within inter photonic space due to the presence of free (unbound) electrons and free (unbound) photons. Similarly, electric potential and photonic potential exist within other states of the material medium as well as within the space medium. The number density of unpaired electrons and unpaired photons in a macro structure may be assumed as the direct function of the number density of paired charge particles in micro domain and micro-micro domain due to mass proportionate imperfections in the structure. Thus, the inter atomic space within a solid, has an electric space charge potential and a photonic space charge potential. Any space pocket contains space matter particles. If the unpaired space matter particle is atomic and sub-atomic particle then the space charge potential and the field are electric in nature. On the other hand, if the space pocket additionally contains unpaired photons, then the space charge potential and the field are photonic in nature. An electric charge particle will interact with the electric charge field whereas the photonic charge particle (light particle) will interact with the photonic charge field. Referring to Fig.7 the space charge potential (photonic charge potential) in inter atomic space of solid is very high due to high density of unpaired photons but the field is zero as there is very little potential gradient. However, a weak photonic field exists only up to a few atomic layers at the surface.
On the other hand, the inter atomic space potential (photonic potential) in gaseous medium is low and the field is also negligible. Thus, there exists a great potential difference across the opposite faces of the interfacing medium. Hence, there exists a very high potential gradient across the thin layer of interface. The thickness of the interface in macro domain scale is zero and that in micro domain scale has a definite value and that again in micro-micro domain scale is very-very large. No micro particle (atomic/sub-atomic particle) finds a placement within the thin interface layer however the interface layer contains space matter particles in micro-micro domain (light particles) both in bound and free state. Due to potential difference across two faces of the interface zone a smooth potential gradient is expected if the medium is resistive but the medium being di-photonic (following the terminology of dielectric) a charge polarized structure appears basing upon the surface of denser medium.
For a transparent material, the potential difference across the interface is relatively small where the polarised field barrier is weak. The polarized photonic structure in the interface zone of opaque and transparent materials is shown in Fig.8. The positively charged light particles while entering normal to the interface experiences repulsion from the positive photonic charge field in addition to the drag forces of the medium. Hence, light particles of different energy levels penetrate to different depths in the interface before its velocity becomes zero. Thereafter, the light particle reverses its direction due to field effect. The normal incident ray is reflected back normal to the surface.
Reflection of light making an angle with the normal
Micro atomic and subatomic particles can have positive, negative or zero electric charge states. Likewise, the micro-micro domain particles (light particles) can have positive, negative or zero photonic charge states. Light particles producing visibility of objects are positively charged photons. Negatively charged photons do not produce visibility of objects, therefore they are not noticed. The vertical component of velocity of light particles is retarded while moving through the positive photonic charge field and is accelerated in the negative photonic charge field.
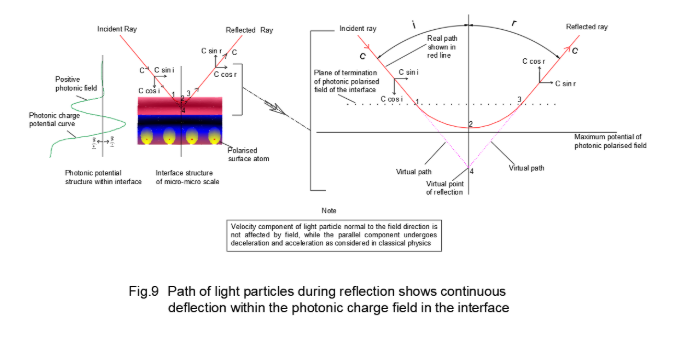
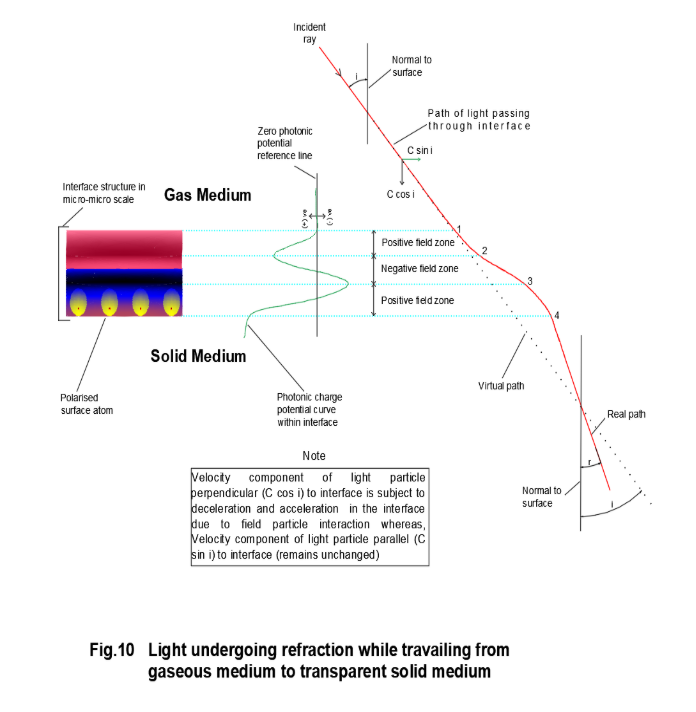
The interface, the field particle interaction and the trajectory of light particles undergoing reflection is shown in Fig.9. The real trajectory is shown in red lines. The incident light ray at an angle ‘i’ with the normal to the interface has two components in mutually perpendicular directions, 1) normal to the surface 2) parallel to the surface. The vertical component of a light particle is decelerated during its transit from point ‘1’ to ‘2’. The velocity becomes zero at point ‘2’. Thereafter the vertical component of the light particle is accelerated during its journey from point ‘2’ to ‘3’. The geometrical details during the transit of light particles from ‘1’ to ‘3’ via point ‘2’ or disappear in macro domain scale, thus giving an illusion of the virtual trajectory following the path 1- 4- 3. The normal component interacts with the field and undergoes deacceleration due to field particle interaction similar to the normal-incident-light discussed above. If the time to reach zero normal velocity is ∆t then the displacement in the direction normal to the interface is Vcos i 2 ×∆t (average velocity time) and the displacement in the direction parallel to the interface is sin i × ∆t. The magnitude of photonic field experienced by the light particle while approaching the interface and leaving the interface remaining same, the time taken for leaving the interface is also ∆t. The normal component of the velocity after time ∆t is equal to -Vcos i . The normal and parallel velocity components at point of approach to the interface are Vcos i and V sin i and at point of leaving the interface are -V cos i and V sin i . Hence, the angle of incidence i is same as the angle of reflection r.
Refraction of light
For photon conducting material (transparent material) the interface is also partially conductive, hence the polarised photonic barrier is small. Thus, light particles easily pass through the field barrier. However, the light particles in their transit through the polarised field of interface undergo field particle interaction where the velocity component of light particle normal to the interface is decelerated in the positive field and subsequently accelerated in the negative photonic field, thereby changing its direction after it passes through the interface. Referring to figure-10, the incident ray inclined at an angle i with the normal enters the interface at point ‘1’ and passes through the positive photonic field between ‘1’ and ‘2’. The normal velocity component of a light particle gradually reduces while passing through the positive photonic field. Hence the magnitude and the direction of the resultant velocity of light particles changes. Thereafter, the light particle enters into the zone of negative photonic field where the normal component of the velocity is accelerated between the points ‘2’ and ‘3’.
If the magnitude of deceleration and acceleration are same then there should not be any change in direction. But this is not the case in refraction of light. The negative field between ‘2’ and ‘3’ being closer to the denser medium, is stronger than the positive field between ‘1’ and ‘2’. Because the net acceleration of the vertical component is more than the net deceleration, the light ray entering a denser medium bends towards the normal after passing through the interface. The reverse phenomena occurs when light ray from a denser medium enters into a rarer medium.
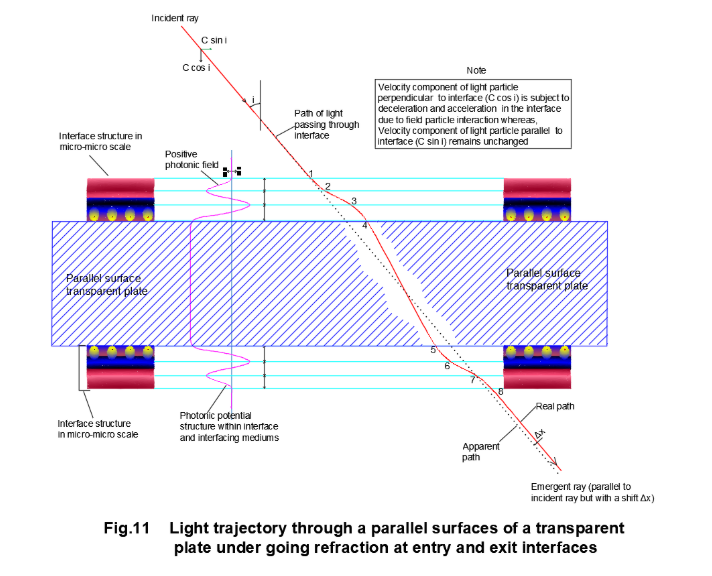
The light particles passing through a parallel transparent material plate experiences both rarer medium to denser medium and denser medium to rarer medium at entry and exit of the parallel plate (Fig.11). The field structure of interface at entry and exit points of a given transparent material being same, the emergent ray becomes parallel to the incident ray with an offset of ∆x. The transit of light particle from rarer medium to denser medium causing refraction is explained by classical dynamics through field particle interaction as it moves from point ‘1’ to ‘4’ and again, the transit from denser to rarer medium is explained by field particle interaction during its motion from point ‘5’ to ‘8’.
Conclusion
The reflection and refraction taking place on a macro surface of zero thickness doesn’t provide any room for analysing the surface effect through classical dynamics since the dimension-less spatial point is a black box that promotes only quantum analysis. The new exploration into finer micro-micro domain and realization of mass, physical structure and non-electric charge of light particles and the fine structure of the medium has successfully provided new understanding of reflection and refraction mechanisms from classical physics point of view. The new perception of micro-micro domain physics and the new state property of light particles and medium has enough scope to deal with other phenomena of light without entertaining duality.
Reference
- https://philosophyofnature.org.in/basic-constituents-of-universe-and-their-interactions.
- https://philosophyofnature.org.in/new-concept-of-electric-charge-in-matter.
- https://philosophyofnature.org.in/electric-and-non-electric-charges-and-their-inter-conversion.
- https://philosophyofnature.org.in/towards-a-new-comprehensive-universal-science.
- https://philosophyofnature.org.in/mass-space-structure-of-centrally-organized-systems.
- https://philosophyofnature.org.in/unified-concept-of-energy-for-all-domains.
- https://philosophyofnature.org.in/modelling-atomic-system.
- https://philosophyofnature.org.in/mechanism-of-formation-of-ionospheric-shells-a-new-concept.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 32, 6968 (1985)\ https://scholar.google.co.in/scholar?q=Physical+Review+B,+Vol.+32,+6968+(1985)&hl=en&as_sdt=0&as_vis=1&oi=scholart.
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/004060907890007X.
- https://philosophyofnature.org.in/new-findings-on-placement-of-orbital-bodies-and-new-characterization-of-motion-of-orbital-celestial-bodies.
Appendix-1
It is not logically correct to declare hydrogen as the absolute lower limit of an atom if reality admits a nucleus smaller than a proton whose spectral signatures overlap with known atoms. Hydrogen is the smallest atom only within the validity of the proton–electron model. If reality contains sub-protonic nuclei, then the present lower limit collapses. Spectral overlap would hide such atoms from detection. Therefore, the “hydrogen limit” is not an absolute truth — only a model-dependent boundary. The present author analyses the feasibility of atoms smaller than hydrogen atoms. Structural similarity exists between atomic systems and the celestial body systems (solar system, planet system, asteroid system etc.) in respect of nucleus and extra-nuclear structure formed by orbital bodies/particles. Recently, the extra nuclear structure has been conceptualised differently as extra-nuclear space structure where the structure is formed in the space matrix containing space matter particles in finer domain and orbital bodies/particles in the same domain as the nucleus but smaller in size [5]. Further, the space matter particles organize different shell-structures with charge features and the orbital celestial bodies are placed in potential cavities resulting in a definite discrete orbit pattern like the discrete orbits of the atomic system [11]. Thus, many similarities are now found existing in the extra nuclear space structures of centrally organized systems in different domains. Hence, it is rational to think that similarity between the structure of the nucleus celestial body and nucleus of an atom also exist without our knowledge of the same. All celestial bodies in the macro domain are composed of atomic matter which are one domain down the domain size of the celestial body. We never assume that large celestial bodies are built up by small celestial bodies (satellites, asteroids, meteors etc.). Even when the mass of the earth is 81 times the mass of the moon, no one says, the earth is made up of 81 moons. Following the structural similarity between the nucleus celestial body and the atomic nucleus, one can as well suggest, the nuclei of atoms are composed of micro-micro domain particles (light particles) particularly when they have physical existence with mass in the new concept. In view of the above, the present structure of the atomic nucleus comprising proton-electron is only a model-based-concept and it may not correspond to the reality of nature. This allows the feasibility of finer and finer atoms below the hydrogen atom. This provides justification for the gradual decrease of the size and the number density of space matter particles towards the boundary.
