INSTITUTE OF PHILOSOPHY OF NATURE
Abstract
Electric charge is seen to exist as the intrinsic property of some micro particles such as proton, electron carrying unit positive and negative charge respectively and different types of quarks carrying fraction of charges. Beyond this we have little knowledge as to how charge appears in matter? What bearing it has with mass and space? Whether charge is a state property of matter (mass-space integral system)? How charge is distributed in the structure of the particle? In the new concept, mass and space are the only two physical entities of the universe and the basic interactions are mass-space, mass-mass and space-space. We have seen how the basic mass-space interactions explain the formation of new extra-nuclear space structure of atom and celestial bodies from mass-space interactions and how the basic interactions is the common cause of both Newtonian gravity and space-time gravity. Unlike Newtonian mass attraction gravity, the new concept of gravity is free from possibility of collapse of the universe. Again, the new mass-space interactions explain why the dense space-matter-particles (atoms and molecules) in the atmosphere of the earth do not settle down to the surface of the earth? Why gravity acts on group of atoms but not to individual atoms? In this article the author argues that electric charge appears in matter in the non-equilibrium state of mass-space association.
Key Words: Cause of Charge, Charge from mass-space structure, Relative charge, Charge state of matter, Positive negative charge is mathematical, Charge neutrality, Mass-space interaction, Gold-leaf experiment.
Introduction
Due to the basic mass-space interactions, matter in any domain, forms a mass-space integral system. If the space holding per unit of mass in all matters in a locality is same then the matters are in a state of mass-space equilibrium where they are neutral to one another. Matters in the state of mass-space equilibrium may be characterized as neutral matters. Any matter having non-equilibrium space holding in a surrounding of neutral matters is an active matter in the surrounding. Matter in active state is referred to as matter carrying charge in the new concept. The author further argues that electric charge is one type where negative and positive values of charge appear in relative scale. Charge interaction appears in matter only in a charge potential difference. The author has analyzed the Gold-Leaf-Experiment and argues that the observed separation of gold leaves is not due to repulsion of the charged gold leaves but due to the charge attraction from so-called neutral bodies from opposite sides. Thus the phenomenon of neutrality of matters in equal potential state is erroneously interpreted in rendering a universal status of neutral matter.
Discussions
Self-existence of electric charge without mass is never found in nature, thus one may argue, electric charge is not a separate physical entity but only a state property of matter. In the new concept, matter in any domain and in any state is a mass-space integral system [1]. Dense mass particles (nuclei of atoms) in a locality capture space in proportion to mass of nuclei due to mass-space attraction where they are in mass-space equilibrium [1]. Matters in the state of mass-space equilibrium are neutral to one another hence they may be referred to as neutral matter with equilibrium space holding. But a neutral matter of one locality having a definite space holding per unit of mass if enters into another locality where the equilibrium space holding per unit of mass is different from that of first locality then the so-called neutral matter becomes an active matter in the new locality. Thus, the phenomenon of neutrality of matter is conditional and not universal. A neutral matter on the surface of the earth may not be a neutral matter on the surface of another celestial body. Hence there is nothing like a universally neutral atom in all frames of reference. Again, the interaction of active matter is only local. Therefore, the neutral atom concept has significance only with respect to a given background condition. Any matter having non-equilibrium space holding in a locality is an active matter in that locality. One may argue, matter in some form of mass-space non-equilibrium in a locality possesses electric charge with respect to the said locality. And further, in this new concept, if the space holding per unit of mass of a micro charge-particle is less than that of its equilibrium value then the charge is positive in a relative scale. On the other hand, if the space holding per unit of mass of a charge-particle is more than that of its equilibrium value then the charge is negative in relative scale. The degree/percentage of shortage or surplus space-holding per unit of mass of the charge-particle compared to neutral matter is the measure of charge potential of the respective charge in the new concept of charge interpreted from mass-space structure of matter.
Matter possesses heat by virtue of its thermal state property (temperature). An electric capacitor possesses electric charge by virtue of its charge state property (voltage). Interesting enough modern science is silent about the charge state of the nucleus of atom or electron by virtue of which the particle holds charge. However, in the new concept of charge, we have scope to know the charge potential as well as the charge of nucleus and electrons.
(equilibrium-space-holding per unit of mass of a neutral particle – space-holding per unit of mass of particle in charge state)
Relative electric Charge potential =——————————————————————————————————————–
(equilibrium-space-holding per unit of mass of neutral particle)
Relative electric charge in a particle = Electric charge potential of the particle x mass of the particle.
Thus, mass rich particles compared to neutral matter carries positive charge and space rich particles compared to neutral matter carries negative charge. Pure space without mass has zero absolute charge and the absolute charge goes on increasing with the increase of mass per unit space holding. Hence in the new concept, matter at any stage has an absolute charge potential. Though neutral matter has zero relative charge potential but it has an absolute charge potential. The characterization of positive and negative charge comes only from the state of the mass-space association therefore both positive and negative charges have one type absolute charge potential, hence one type of charge. This is in contrast to the existing concept of two types of charges. Subsequently we shall see as to how the so-called two types of charges, in reality, is only one type.
The atoms on the surface of the earth are neutral to one another. All atoms have nuclei and extra-nuclear structures. In the new concept, the extra-nuclear structure of atom comprises a space density graded space structure containing space matter particles and orbital particles (electrons) [2]. If we remove the extra-nuclear structure of an atom, then the bare nucleus with reduced space holding per unit of mass becomes positively charged. Then it becomes obvious that the extra-nuclear structure as a whole possesses negative charge. Any partial loss of extra-nuclear structure of an atom makes the remaining atom a positive ion. The lost extra-nuclear structure contains compact space with space-matter particles and orbital electrons. The nucleus of an atom is a mass rich particle with lower space holding per unit of mass as compared to that of atom with equilibrium space holding. Both the compact space with space matter particles and the electrons have more space holding per unit mass as compared to that of neutral atom. Relatively the nucleus of atom is a mass rich particle and the electrons are space rich particles. In the new concept, both positive and negative charges are caused due to non-equilibrium space holding per unit of mass. Hence, the mass content per unit of space-holding is the measure of absolute charge state of matter which becomes positive or negative when characterized in a charge relative scale. A positive charge characterized in a low charge potential locality becomes a negative charge when shifted to a high charge potential locality. Neutral matter with zero relative charge has definite mass content per unit of space holding hence has definite absolute charge potential and absolute charge. Neutralization of positive and negative charges is feasible only if the charges are one type. This implies, charge neutralization is not feasible if the charges are different types. For example: The vacancy created by removing a mango from a fruit basket cannot be replenished by putting an apple in the vacancy.
Neutralization of thermal potential (temperature) takes place by mixing hot matter and cold matter. This is feasible because the positive temperature and negative temperature in relative scale is one type of thermal property in absolute scale. Both electrical and thermal interactions take place in respective potential differences. The interaction between positive and negative charges is in agreement with the interaction in a potential difference. The repulsion of similar charges at same potential is a strong proof for existence of two types of charges. How can the electric charge be one type for some purpose and be two types for some other purpose? Experimental evidences cannot go wrong. Thus an electric charge has to be one type for neutralization of positive and negative charges and again the electric charges has to be dissimilar to justify: similar charges repel & dissimilar charges attract. The above characterization is backed by experimental evidence. However, this author argues, an experimental observation may lead to erroneous conclusion if the interpretation of experimental result is not proper. The present author reviewed the Gold-Leaf Experiment to find any possible error in the interpretation of Gold-Leaf Experiment.
New interpretation of Gold-Leaf Experiment
A simple gold-leaf electroscope is shown in Fig.1. It consists of two strips of very thin gold leaves G1 and G2 suspended side by side from the lower end of the brass rod C which carries a flat brass disc D at its upper end and is supported by an ebonite insulator.
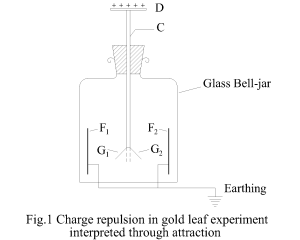
The leaf system is protected by a glass bell jar. On the inner wall of the bell jar and facing the gold leaves there are two strips of tin foils F1 and F2. The tin foils at the inner wall are connected to the external terminal and are earthed. Now if a charged body is brought in contact with the disc D then some charge from the charged body will be conducted to the disc and then into the leaves. When the leaves get charged, the leaves G1 and G2 are attracted towards F1 and F2 respectively due to the charge potential difference. The attraction potential between G1 and G2 as well as F1 and F2 are zero due to equal potential condition. The gold leaf G1 gets attracted towards the nearest tin plate F1 and gold leaf G2 gets attracted towards the nearest tin plate F2 due to charge attraction in a charge potential difference. One can as well proceed to find the independent motion of G1 and G2 from the differential charge field in the surrounding medium even without the presence tin plates.
Scientists aiming to study the interaction of similar charges in the designed experiment see only the mutual separation of gold leaves because they are already expecting a mutual charge interaction, thus giving them motivation to conclude that similar charges repel. On the other hand, this author, with the new postulate that the charge interaction takes place only at a charge potential difference, sees that the gold leafs are attracted towards the tin foils having potential difference. And the mutual interaction between G1 and G2 is zero due to equal potential state. Now the experiment remaining same the earlier conclusion of repulsion of similar charges can be described as, similar charges behave neutral to one another. Here we notice, what we intend to find often influence our mid to note what we found. Attraction of positive and negative charges agrees with the charge interaction in a potential difference and the charges are of same type. But repulsion of similar charge is established from the results of Gold-Leaf-Experiment. This author argues that the gold-leaves at same electric potential do not repel one another however; the gold leaves are separated from one another being pulled by so-called neutral matter from opposite sides finding a potential difference. With the preconceived concept of neutral matter with absolute zero charge at absolute zero charge potential, the cause of separation of gold leaves is erroneously attributed to the charge interaction between the charged gold plates.
Conclusion
We formulate a relative scale by assuming certain absolute value as zero for the relative scale. Thus in relative scale, any absolute value below the absolute value assumed zero for the relative scale becomes negative. Negative value is not feasible in the absolute scale. For example: if 4 mangos (absolute numbers) are there on a table then no one can take 5 mangos from the table leaving one negative (-1) mango on the table. The values of any one type of property may appear positive or negative when expressed in a relative scale. Unit positive and unit negative values of any single property have the ability to neutralize one another. It is a known fact that one unit of positive electric charge neutralizes one unit of negative electric charge. Proton having + 1 electronic charge when combines with an electron having – 1 electronic charge forms a neutron with zero charge. This confirms that the +ve and –ve charges are one type and again the charge values are expressed in a relative scale. The statement that similar charges repel and dissimilar charges attract implies that the electric charges are of two types. The author hear argues that matter carries absolute charge at absolute charge potential. Charge interaction takes place only in a charge potential difference and matters at same charge potential i.e. without a potential difference are neutral to one another. The repulsion of similar charge established from gold leaf experiment can be interpreted differently to show that similar charges do not repel. Electric charge, rather in the new concept, appears in matter in non-equilibrium state of mass-space association which acknowledges the electric charge is one type.

In this article, the new way of explanation of electric charge with gold leaf experiment really very nice.
This perspective on electric charge as arising from non-equilibrium states of mass-space association offers a novel approach to understanding the fundamental state properties of matter.